Digital tools are increasingly being applied to support the response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic in India and elsewhere globally.
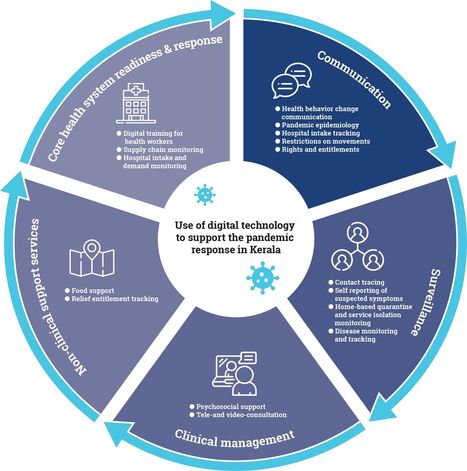
This article draws from global frameworks to explore the use of digital tools in the state of Kerala across the domains of communication, surveillance, clinical management, non-clinical support, and core health system readiness and response.
Kerala is considered India’s first digital state, with the highest percentage of households with computers (24%) and the internet (51%) in India, 95% mobile phone penetration, 62% smartphone penetration and 75% digital literacy. Kerala has long been a model for the early adoption of digital technology for education and health.
As part of the pandemic response, technology has been used across private and public sectors, including law enforcement, health, information technology and education. Efforts have sought to ensure timely access to health information, facilitate access to entitlements, monitor those under quarantine and track contacts, and provide healthcare services though telemedicine.
Kerala’s COVID-19 pandemic response showcases the diverse potential of digital technology, the importance of building on a strong health system foundation, the value of collaboration, and the ongoing challenges of data privacy and equity in digital access.
Summary
-
The COVID-19 pandemic’s unprecedented global spread and impact has accelerated interest in digital innovation.
-
Kerala’s experience showcases the diverse and innovative ways that digital tools can build on a strong underlying health system to support pandemic response across the domains of communication, surveillance, clinical management, non-clinical support and core health system readiness.
-
Digital tools in Kerala were able to proliferate rapidly and help meet diverse citizen needs due to high levels of collaboration and intersectoral response that brought together different levels of government and multiple state departments, engaged the private sector, and harnessed the energy of civil society organisations and community volunteers.
-
Digital technology has great potential to strengthen public health measures during pandemics, including to rapidly link citizens to food and mental health support.
-
Adequate oversight and community participation remains essential to safeguard citizen privacy and ensure equity.
read the open access paper at https://gh.bmj.com/content/6/Suppl_5/e005355



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...