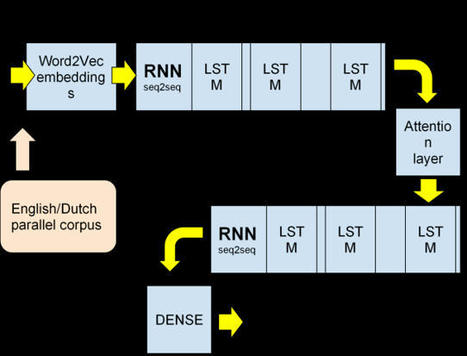
Google Translate works so well, it often seems like magic. But it’s not magic — it’s deep learning!
In this series of articles, we’ll show you how to use deep learning to create an automatic translation system. This series can be viewed as a step-by-step tutorial that helps you understand and build a neuronal machine translation.
This series assumes that you are familiar with the concepts of machine learning: model training, supervised learning, neural networks, as well as artificial neurons, layers, and backpropagation.
In this article, we’ll examine the tools we'll need to use to build an AI language translator.
Multiple frameworks provide APIs for deep learning (DL). The TensorFlow + Keras combination is by far the most popular, but competing frameworks, such as PyTorch, Caffe, and Theano, are also widely used.
These frameworks often practice the black box approach to neural networks (NNs) as they perform most of their "magic" without requiring you to code the NN logic. There are other ways to build NNs — for instance, with deep learning compilers.
The following table lists the versions of the Python modules we’ll use. All these modules can be explicitly installed using the ==[version] flag at the end of a pip command. For instance: "pip install tensorflow==2.0".
The code we're writing should work on any operating system but note that we're using Python 3, so make sure you have it installed. If your system has both Python 2 and Python 3 installed, you'll need to run pip3 instead of pip in the install commands below:
module version TensorFlow 2.3.1 Keras 2.1.0 numpy 1.18.1 pandas 1.1.3 word2vec
0.11.1
read the entire article for the list of instructions at https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/5299747/Tools-for-Building-AI-Language-Translation-Systems



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...