The COVID-19 pandemic is the greatest public health crisis of the last 100 years. Countries have responded with various levels of lockdown to save lives and stop health systems from being overwhelmed. At the same time, lockdowns entail large socioeconomic costs.
One exit strategy under consideration is a mobile phone app that traces the close contacts of those infected with COVID-19.
Recent research has demonstrated the theoretical effectiveness of this solution in different disease settings. However, concerns have been raised about such apps because of the potential privacy implications. This could limit the acceptability of app-based contact tracing in the general population. As the effectiveness of this approach increases strongly with app uptake, it is crucial to understand public support for this intervention.
Objective: The objective of this study is to investigate the user
acceptability of a contact-tracing app in five countries hit by the pandemic.
Methods: We conducted a largescale, multicountry study (N=5995) to measure public support for the digital contact tracing of COVID-19 infections.
We ran anonymous online surveys in France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, and the United States and measured intentions to use a contact-tracing app across different installation regimes (voluntary installation vs automatic installation by mobile phone providers) and studied how these intentions vary across individuals and countries.
Results: We found strong support for the app under both regimes, in all countries, across all subgroups of the population, and irrespective of regional-level COVID-19 mortality rates.
We investigated the main factors that may hinder or facilitate uptake and found that concerns about cybersecurity and privacy, together with a lack of trust in the government, are the main barriers to adoption.
Conclusions:
Epidemiological evidence shows that app-based contact tracing can suppress the spread of COVID-19 if a high enough proportion of the population uses the app and that it can still reduce the number of infections if uptake is moderate. Our findings show that the willingness to install the app is very high. The available evidence suggests that app-based contact tracing may be a viable approach to control the diffusion of COVID-19.
read the study at https://mhealth.jmir.org/2020/8/e19857

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...



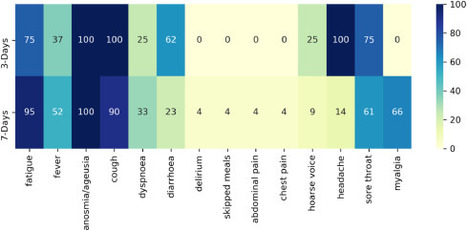




A lot of research and anecdotal evidence shows that mHealth/Mobile App based contact tracing can suppress the spread of COVID-19 if a high enough proportion of the population uses the app.
that it can still reduce the number of infections if uptake is moderate is interesting to note.